Supports Muscle Strength & Power Output
More Strength. More Power. More You.
Creatine That Works as Hard as You Do.
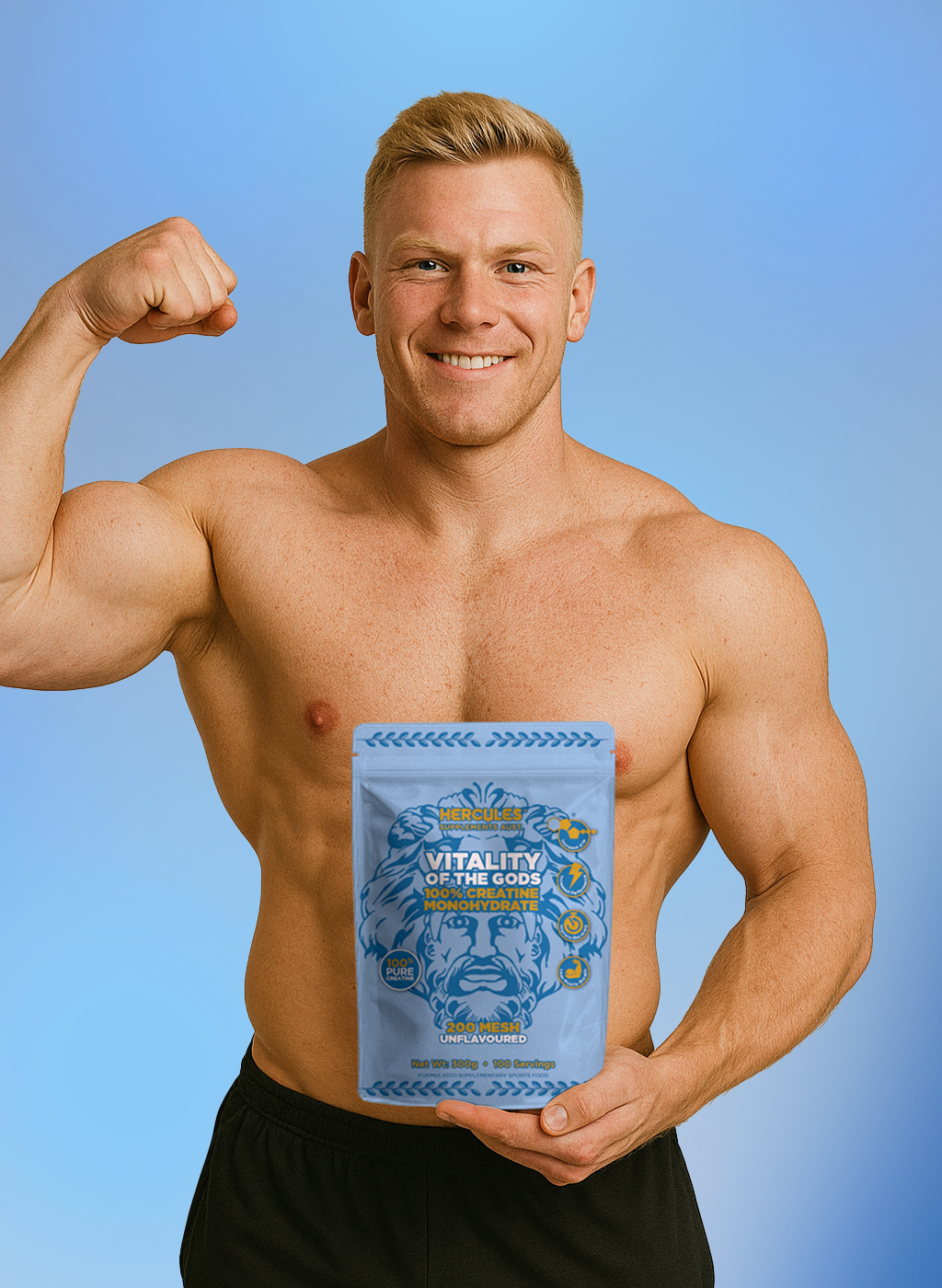
Vitality of the Gods - Creatine Monohydrate Powder
Vitality of the Gods - Creatine Monohydrate Powder
MUSCLE STRENGTH
Supports muscle strength and power output

INTENSE TRAINING
Increases energy for high intensity training.

MUSCLE GROWTH & PERFORMANCE
Supports strength, endurance, and recovery for peak physical performance.
MIND & MUSCLE HEALTH
Creatine supports not only physical performance but also brain health, enhancing mental clarity and cognitive function.
Description
Description
We don’t believe creatine should be gritty, hard to mix, or loaded with fillers. You shouldn’t have to choke it down, guess if it’s working, or question the quality. It should be clean, smooth, and reliable, every single time.
That’s why we created Vitality of the Gods: Creatine Monohydrate. A pure, ultra-micronised Creatine Monohydrate designed to support strength, muscle growth, performance, and even cognitive function like memory and focus. Zero fillers, zero flavouring, and no gritty texture.
Vitality of the Gods: Creatine Monohydrate isn’t just a performance add-on it’s a daily essential for lifting heavier, thinking sharper, and recovering better.
How To Use
How To Use
Mix 1–5 scoops with 250–300 ml of water or your favourite beverage. Consistent use for 180 days is recommended for optimal results and to achieve long-term physical benefits.
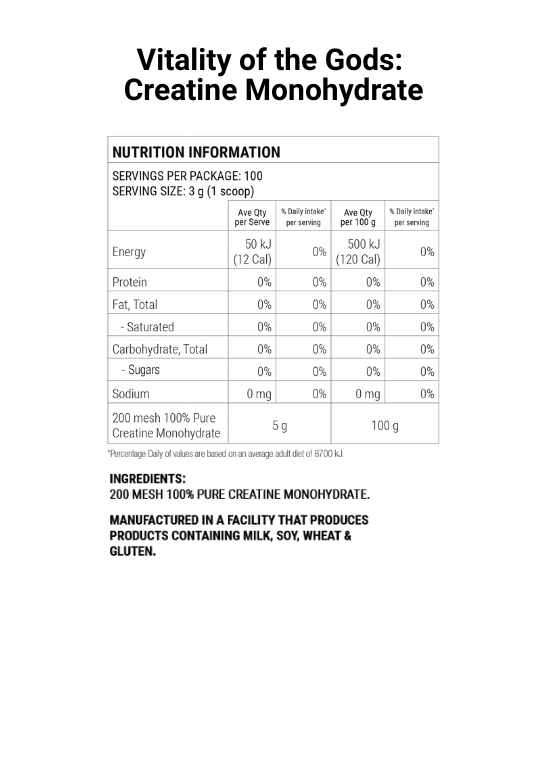
Nutritional Information
Nutritional Information
Flavours Explained
Flavours Explained
Vitality of the Gods: Creatine Monohydrate is unflavoured. We advise mixing it with your favourite beverage for best taste.
What Our Hercules Family Are Saying
What Our Hercules Family Are Saying
We analysed thousands of verified reviews to uncover exactly what our customers love and what’s actually delivering results.
This isn’t theory. It’s real feedback from real people getting real outcomes.
94% reported increased strength or endurance within 2 weeks
93% noticed improved gym performance or power output
85% said it helped them break training plateaus
91% stacked it with pre or post-workout products
20,000+
500,000+
1M+
100+








Why Our Creatine Actually Works:
We Use What Delivers — Not What’s Cheap.





























